装卸工 : ClassLoader
作为勤劳的底层员工,ClassLoader是生产过程的重要保障,它会将需要的Class字节码文件装载到内存当中,为程序的执行做准备工作。
上一篇我们知道了,类加载器ClassLoader分为Bootstrap ClassLoader(启动类装载器)、ExtClassLoader(扩展类装载器)和AppClassLoader(应用类装载器),除了启动类装载器之外,其余的类加载器都必须继承java.lang.ClassLoader类。那么,我们先从java.lang.ClassLoader类开始分析吧。
关于java.lang.ClassLoader类
官方的说明如下:
/**
* A class loader is an object that is responsible for loading classes. The
* class <tt>ClassLoader</tt> is an abstract class. Given the <a
* href="#name">binary name</a> of a class, a class loader should attempt to
* locate or generate data that constitutes a definition for the class. A
* typical strategy is to transform the name into a file name and then read a
* "class file" of that name from a file system.
**/大概的意思就是:
- 类加载器是一个负责加载类的对象。
- ClassLoader是一个抽象类。
- 当给定一个类的二进制名称,类加载器应该尝试找到或生成构成class定义的数据。一个典型的策略是把名字转换成文件名,然后读一个文件系统中该名称的“class文件”。
loadClass 方法
作为所有类加载器的父类,ClassLoader类中包含了很多公用的方法,其中比较重要的是loadClass(String name, boolean resolve),这方法是加载Class文件的关键。
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}这个方法拥有两个参数,name表示需要加载的类的二进制名称,resolve表示是否需要和本地类进行关联。
我们从源码中可以看出,整个加载类的方法都是同步(synchronized)的,也就是说除非被重写,这个方法默认在整个装载过程中都是同步的(线程安全的)。
getClassLoadingLock
我们遇到的第一个方法是:getClassLoadingLock(name),按照官方注解的说法这个方法是Returns the lock object for class loading operations.,意思是:返回类加载操作的锁定对象。
protected Object getClassLoadingLock(String className) {
Object lock = this;
if (parallelLockMap != null) {
Object newLock = new Object();
lock = parallelLockMap.putIfAbsent(className, newLock);
if (lock == null) {
lock = newLock;
}
}
return lock;
}从源码,我们可以发现,所谓的所对象其实就是一个Object,而parallelLockMap是ClassLoader的不可变属性,当我们所需加载的类的锁存在于这个map中的时候就会返回相应的锁对象,如果锁对象不存在,则创建一个新的锁对象。
当然,根据源码来看这个parallelLockMap并不简单,它在ClassLoader类初始化的时候被创建的:
private ClassLoader(Void unused, ClassLoader parent) {
this.parent = parent;
if (ParallelLoaders.isRegistered(this.getClass())) {
parallelLockMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
package2certs = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
domains =
Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<ProtectionDomain>());
assertionLock = new Object();
} else {
// no finer-grained lock; lock on the classloader instance
parallelLockMap = null;
package2certs = new Hashtable<>();
domains = new HashSet<>();
assertionLock = this;
}
}这大段代码看得人一脸懵逼,其实根据官方注释来看,实际上这一大段就实现了一个功能:类加载器的并行处理能力。
当类加载器在ParallelLoaders中注册了并行处理能力,那么
parallelLockMap就会有实例,即此类加载器拥有并行处理能力。那么上面获取类加载器锁定对象的时候就可以从parallelLockMap中获取了,如果类加载器没有并行处理能力,那么在获取锁定对象的时候就会直接返回类加载器对象。
findLoadedClass
这个方法用于查找指定的类是否已经被加载过了,具体的实现是由本地方法实现的。
loadClass
为什么又到这个方法了呢?实际上这里调用的是父类的loadClass方法,这里的ClassLoader使用了双亲委托机制。
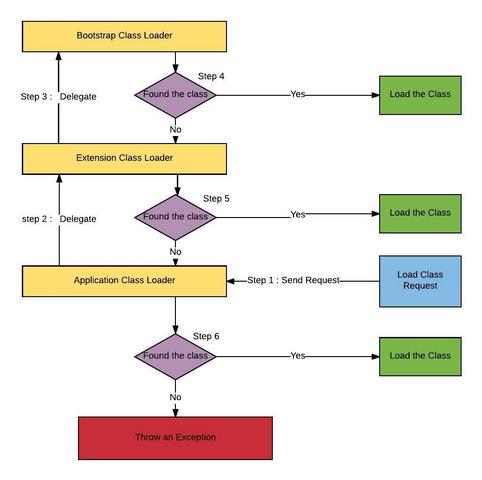
关于双亲委托机制网上有很多文章介绍,所以我就不赘述了,简单来说就是装载器有载入类的需求时,会先请示其父装载器使用其搜索路径帮忙载入,如果父装载器找不到,那么才由自己依照自己的搜索路径搜索类。
关于双亲委托机制,可以参考以下文章:
其他
关于loadClass方法,虽然它是由protected修饰的,但是官方并不推荐子类重写该方法。因为该方法中的双亲委托机制是对jdk中已有的类进行保护,避免用户的类与jdk中已有的类产生冲突。如果用户需要修改类加载的机制,推荐对findClass方法进行重写。
findClass 方法
抽象类,由装载器的子类进行实现,用于寻找类的字节码文件。会抛出java.lang.ClassNotFoundException异常。
defineClass 方法
最终实现类的加载和定义的方法,将由findClass方法寻找找到字节码文件的字符数组进行加载转换成java类。会抛java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError异常
最后
总结一下类加载的过程:
结束
本文部分文本来源于互联网
感谢以下文章提供的灵感和帮助